API Performance Testing: A Step-by-Step Guide
Table of Contents
Ever clicked “Buy Now” and watched the spinner spin endlessly? That moment of silence isn’t just frustrating; it’s costly. Behind the scenes, an API may be struggling to keep up, and when APIs fail to perform, users abandon transactions, conversions drop, and trust breaks up.
APIs are the backbone of modern applications. They connect apps, power features, and keep data flowing. But when traffic spikes or systems scale, even the best APIs can struggle to keep up. That’s where API performance testing comes in as a business-critical safeguard.
This guide will walk you through the essentials of API performance testing – what to test, how to test, and how to turn raw data into actionable insights to ensure your API is fast, resilient, and scalable. So, without waiting any more, let’s get into it.
What Is API Performance Testing?
Think of API performance testing as a stress test for your digital backbone. It’s how you make sure your APIs don’t just work – they work fast, scale well, and stay cool under pressure. Whether it’s a checkout flow, a login endpoint, or a data sync with a third-party service, performance testing simulates real-world traffic to see how your APIs behave when things get intense.
In short, it’s about preparation, not perfection. You’re testing critical metrics – response times, throughput, error rates, and resource usage – before your users experience failures.
Why Does API Performance Testing Matter?
API performance testing isn’t just about speed; it’s about reliability, scalability, and trust. Here’s what makes it essential:
-
Ensures High Availability and Uptime
Your users expect your app to be available 24/7. Performance testing helps you simulate real-world traffic and stress conditions so you can catch issues before they cause downtime. Because “site unavailable” is never a good look.
-
Identifies Blocks before Deployment
Why wait for production to reveal a slow endpoint or a memory leak? Testing early helps you pinpoint inefficiencies in code, infrastructure, or third-party services, before they impact users or revenue.
-
Validates SLAs and Performance Benchmarks
Whether you’re promising a 200ms response time or relying on a vendor’s uptime guarantee, performance testing gives you the data to back it up. It’s how you move from assumptions to accountability.
-
Improves End-User Experience
Speed isn’t just a technical metric; it’s a user emotion. Fast APIs mean smoother interactions, quicker checkouts, and happier customers. And in E-commerce, milliseconds can make the difference between a sale and an abandoned cart.
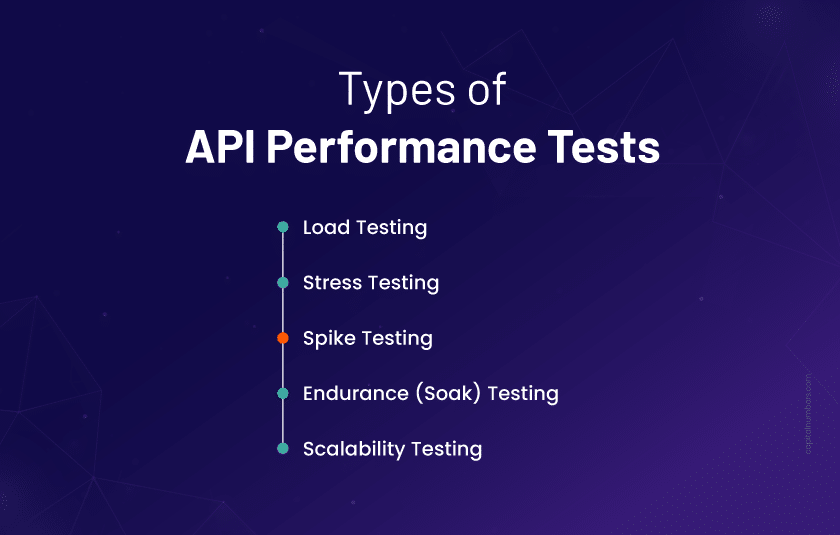
Types of API Performance Tests
Not all performance issues show up under normal conditions. That’s why API testing needs to simulate a range of real-world scenarios, from steady traffic to sudden surges. Here are the five core types of tests that help you uncover how your API behaves under pressure:
-
Load Testing
Purpose: Measures how your API behaves under expected and peak traffic conditions.
Why it matters: Load testing is the foundation of API performance testing. It helps you understand how your system handles concurrent users, request volumes, and data loads – using real-life scenarios.
Pro tip: Use API test automation tools like Postman, JMeter, or k6 to simulate traffic and monitor key API performance metrics like response time, throughput, and error rate.
-
Stress Testing
Purpose: Pushes your API beyond its capacity limits to find the breaking point.
Why it matters: It’s not just about failure; it’s about how gracefully your system fails. Stress testing helps you identify memory leaks, unhandled exceptions, and infrastructure weaknesses before they hit production.
Best for: Mission-critical APIs where downtime isn’t an option.
-
Spike Testing
Purpose: Tests how your API reacts to sudden, extreme surges in traffic.
Why it matters: Think flash sales, viral campaigns, or unexpected user spikes. Spike testing reveals how quickly your API can scale up and recover without crashing or slowing down.
Tip: Combine with real-time API monitoring to track performance metrics during the spike and cooldown phases.
-
Endurance (Soak) Testing
Purpose: Evaluates long-term stability by running the API under sustained load for hours or even days.
Why it matters: Some issues, like memory leaks or database connection exhaustion, only surface over time. Soak testing ensures your API can handle continuous usage without degradation.
Ideal for: APIs supporting 24/7 services or high-volume ecommerce platforms.
-
Scalability Testing
Purpose: Assesses how well your API scales horizontally (adding servers) or vertically (upgrading resources).
Why it matters: As your user base grows, your infrastructure needs to keep up. Scalability testing helps you plan capacity, optimize cloud resources, and ensure consistent performance.
Use case: API development companies often include this in their CI/CD pipelines to future-proof applications.
Key Metrics to Consider for API Performance Testing
When it comes to maximizing API performance, metrics are your compass. They help you understand how your API behaves under pressure, where it slows down, and how it scales. Here, we have listed down the key metrics to consider:
-
Response Time and Latency
This metric measures the time it takes the API to respond to a request.
- Response time includes processing and network delays.
- Latency refers to the time it takes for a request to reach the server and return.
-
Throughput (Requests per Second)
Tracks how many requests your API can handle per second under load. High throughput means your API can serve more users simultaneously, which is critical for scaling and load balancing. It is often used in API load testing to simulate real-world traffic.
-
Error Rate and Timeout Percentage
Monitors the percentage of failed requests or those that exceed acceptable response times. A rising error rate during stress or spike testing signals instability. Timeouts often indicate blocks in backend services or network delays.
-
CPU, Memory, and Network Usage
It evaluates how efficiently your infrastructure supports API traffic.
- High CPU or memory usage may point to inefficient code or resource leaks.
- Network usage helps detect bandwidth constraints or latency issues.
These metrics are essential for tuning performance and planning capacity.
-
Peak Load Tolerance
It defines the maximum traffic your API can handle before performance degrades. Also, it helps set realistic SLAs (Service-Level Agreements) and guides decisions around horizontal or vertical scaling. This metric is often measured during stress and scalability testing.
Step-by-Step API Performance Testing Process
A solid API performance testing strategy isn’t just about running scripts; it’s about building confidence in your system’s ability to scale, recover, and deliver consistently. Whether you’re working with an API development company or managing in-house testing, here’s how to do it right:
Step 1: Define Objectives and SLAs
Start with clarity. What does “fast” or “reliable” mean for your business?
- Set measurable KPIs like max 2-second response time, 99.9% uptime, or <1% error rate.
- These benchmarks guide your entire testing process and align with business expectations.
Step 2: Choose the Right Tools
Select API performance testing tools that match your stack and scale.
- Open-source options: JMeter, Postman, K6, Locust, Gatling
- Commercial platforms: BlazeMeter, LoadRunner, ReadyAPI
- Consider ease of integration, reporting features, and support for API test automation.
Step 3: Design Test Scenarios
Build realistic simulations that reflect actual user behavior.
- Identify critical endpoints (e.g., login, checkout, search).
- Include authentication flows, varied payloads, and concurrent users.
- Think beyond happy paths, test edge cases, and peak usage patterns.
Step 4: Set Up the Test Environment
Your test results are only as good as your setup.
- Mirror production conditions as closely as possible.
- Include network latency, database load, and third-party dependencies.
- Use staging environments with similar configurations to avoid false positives.
Step 5: Execute Performance Tests
Run your tests incrementally to observe how the API handles increasing load.
- Start with baseline loads, then ramp up to stress and spike levels.
- Monitor API health, response times, and system behavior during peak traffic.
Step 6: Monitor and Analyze Results
Use dashboards, logs, and analytics to interpret the data.
- Track key API performance metrics: response time, throughput, error rate, and resource usage.
- Identify blocks, slow endpoints, and failure points.
- Tools like Grafana, New Relic, or DataDog can help visualize trends.
Step 7: Optimize and Retest
Turn insights into action.
- Apply fixes: code optimization, caching strategies, and infrastructure scaling.
- Re-run tests to validate improvements and ensure issues are resolved.
- Document results to build a performance baseline for future releases.
Best Practices for API Performance Testing
Great API performance doesn’t happen by accident; it’s engineered through consistent testing, smart tooling, and disciplined workflows. Here are the best practices to help you stay ahead of performance issues and deliver seamless user experiences.
-
Test Early and Continuously (Shift-Left Approach)
Don’t wait until deployment to test performance. Integrate API performance testing early in the development cycle to catch issues before they become expensive. Shift-left testing helps teams build faster, more reliable APIs from day one.
-
Automate Performance Tests Within CI/CD Pipelines
Embed API test automation into your CI/CD workflows to ensure every build meets performance standards. Automated tests help maintain speed, scalability, and uptime across releases without manual intervention.
-
Use Version Control for Test Scripts
Treat your test scripts like production code. Store them in Git or other version control systems to track changes, collaborate across teams, and maintain consistency. This is especially useful when working with multiple environments or external partners.
-
Monitor in Real-Time During Tests
Use dashboards and observability tools to track API performance metrics, such as response time, error rate, and resource usage, while tests are running. Real-time API monitoring helps you spot blocks instantly and correlate issues with system behavior.
-
Document Results for Audit and Regression Testing
Keep a record of test outcomes, configurations, and fixes. This documentation supports audits, supports regression testing, and establishes a performance baseline for future releases. It also ensures transparency across dev, QA, and business teams.
Common Mistakes to Avoid during API Performance Testing
Even the best testing strategy can fall short if key details are overlooked. Here are some common pitfalls that can impact your results or leave critical gaps in your API performance testing process:
-
Ignoring Authentication or Rate Limits
Skipping authentication flows or hardcoding tokens might speed up test setup, but it doesn’t reflect how real users interact with your API. Also, overlooking rate limits can lead to false positives or missed throttling issues, especially when working with third-party APIs.
-
Testing Only Under Ideal Network Conditions
Running tests on a high-speed local network won’t reveal how your API performs for users on slower or unstable connections. To maximize API performance in the real world, simulate variable latency, packet loss, and bandwidth constraints.
-
Not Cleaning Up Test Data
Leaving test records in your database can affect it, skew analytics, and even trigger false alerts. Always include teardown steps in your API test automation scripts to maintain clean, reusable environments.
-
Failing to Simulate Realistic User Behavior
Testing a single endpoint in isolation doesn’t reflect how users actually use your app. Design test scenarios that mimic real workflows like login → browse → add to cart → checkout – with varied payloads and concurrency. This helps uncover issues that only surface under complex, multi-step interactions.
You May Also Read: Complete Guide to API Testing: Methods and Best Practices
Bottom Line
API performance testing isn’t just a technical checkbox; it’s a business safeguard. Every millisecond saved, every block removed, and every spike handled gracefully translates into smoother user experiences, stronger conversions, and scalable growth.
Whether you’re launching a new feature, prepping for a flash sale, or integrating with mission-critical services, testing your APIs under load is how you stay ahead of surprises. Because in the real world, traffic doesn’t wait, users don’t retry, and trust isn’t easily rebuilt. So test smart. Test often. And build APIs that perform like champions, even when the pressure is on.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What’s the difference between API performance testing and functional testing?
Functional testing checks if your API works correctly. Performance testing checks how well it performs under stress, such as high traffic, large payloads, or slow networks.
2. How do I know if my API is performing well?
Compare your metrics against SLAs or internal benchmarks. For example, a good response time is typically under 300ms for critical endpoints.
3. Can performance testing help with scalability?
Absolutely. It reveals how your API behaves as load increases, helping you plan for horizontal scaling, caching, or architectural changes.
4. Should I test third-party APIs too?
You can’t control them, but you should test how your system handles delays, failures, or rate limits from external APIs.
5. How often should I revisit performance tests?
Regularly, especially after updates, infrastructure changes, or traffic growth. Performance isn’t a one-time check; it’s ongoing maintenance.