A Guide to Cloud Service Models: How IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS Benefit Your Business
Table of Contents
Cloud computing is reshaping how businesses operate by offering flexible, cost-effective cloud solutions for managing data, applications, and infrastructure. These innovations are made possible through three main types of cloud service models that are driving this transformation: IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), and SaaS (Software as a Service).
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources like servers and storage, allowing businesses to manage their infrastructure. PaaS offers a platform to build and deploy applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. SaaS delivers ready-to-use applications over the internet, allowing businesses to focus on using the software rather than managing it.
These cloud service models are helping companies of all sizes streamline operations, scale efficiently, and innovate faster. To better understand how these cloud service models contribute to business success, let’s take a closer look at each model, its unique benefits, and how it can be leveraged to optimize operations, reduce costs, and enhance scalability.
What is Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud service model that provides virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, over the Internet. Instead of investing in costly physical hardware, you can rent these IT resources on-demand, allowing you to scale your infrastructure easily based on your needs.
Key Features:
- Scalability: With IaaS, you can easily scale up or down based on your needs. Whether you’re handling a sudden surge in traffic or reducing resources during off-peak times, IaaS allows you to adjust seamlessly.
- Flexibility: You have full control over how you configure and manage your infrastructure, enabling you to tailor cloud solutions to your business requirements.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing: IaaS follows a pay-as-you-go model, meaning you only pay for the resources you use. This helps you save on costs and ensures you’re not paying for unused capacity.
Common Use Cases:
- Hosting websites and applications: IaaS makes hosting websites, web applications, and databases simple without worrying about the underlying hardware.
- Data storage and backups: IaaS offers secure, scalable storage solutions, ensuring your data is backed up and readily available whenever needed.
- Disaster recovery: IaaS allows you to set up disaster recovery systems to protect your business from data loss or system failures, minimizing downtime.
- Development and testing: With IaaS, developers can quickly create virtual environments for testing, deploying, and scaling applications, without the need for physical infrastructure.
Examples of IaaS Providers:
- AWS (Amazon Web Services): AWS is a leading cloud provider offering an extensive suite of IaaS products, including Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) for scalable computing power and Simple Storage Service (S3) for secure data storage. Its wide range of services and global infrastructure make it highly suitable for businesses that require flexibility and scalability worldwide.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure stands out for its seamless integration with Microsoft’s software ecosystem, making it a top choice for businesses that rely on Windows Server, Active Directory, or SQL Server. It offers robust IaaS solutions such as Virtual Machines and Blob Storage, with strong security and compliance features tailored for enterprises.
- Google Cloud Platform: Google Cloud excels in providing high-performance computing and machine learning capabilities. Its IaaS offerings, like Compute Engine and Cloud Storage, are optimized for big data analytics and AI workloads, making it ideal for businesses focusing on advanced technologies and data-intensive applications.
If you’re looking for flexibility and cost-efficiency, IaaS is the ideal choice for your business. It allows you to scale resources on-demand, eliminating the need for costly physical infrastructure and enabling you to focus on growth and innovation.
You May Also Read: AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud Platform: A Detailed Comparison
What is Platform as a Service (PaaS)?
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud service model that provides a platform to develop, run, and manage applications without the need to manage the underlying infrastructure. It allows businesses to focus on application development, while the platform takes care of scaling, security, and infrastructure management.
Key Features:
- Development Frameworks: PaaS provides built-in frameworks and tools to streamline application development and deployment. These tools help developers save time and effort, allowing them to focus on creating value for the business rather than managing infrastructure.
- Managed Services: With PaaS, essential services like databases, load balancing, and messaging systems are fully managed, reducing the overhead for your IT team. This allows businesses to quickly deploy solutions without worrying about the complexities of managing hardware.
- Auto-Scaling: PaaS solutions automatically adjust your applications based on traffic or resource needs, offering flexibility and efficiency. This helps optimize cloud expenses, ensuring you only pay for the resources you use.
Common Use Cases:
- Application Development and Deployment: PaaS is ideal for businesses seeking to rapidly build, test, and deploy applications in a highly scalable and managed environment, reducing the complexity of infrastructure management.
- Microservices Architecture: With PaaS, you can design modular applications using microservices, allowing independent scaling and management of each component, making updates and scaling more efficient.
- API Management: PaaS platforms provide the tools to create, deploy, and manage APIs, offering a seamless way to integrate with other systems and applications.
- Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): PaaS simplifies the CI/CD pipeline, offering automation for testing, integration, and deployment. This enhances productivity, accelerates release cycles, and ensures higher quality software.
Examples of PaaS Providers:
- AWS Lambda: AWS Lambda allows you to run code without provisioning or managing servers. This serverless architecture supports cloud solutions for business by enabling event-driven applications that scale automatically.
- Google App Engine: Google App Engine provides a fully managed platform for building and deploying applications on Google’s infrastructure. It automates the scaling process and integrates with other Google Cloud solutions.
- IBM Cloud: IBM Cloud offers a robust platform that supports containerized applications and provides the flexibility to run legacy systems or modern applications. It offers enterprises a comprehensive platform for cloud service types like PaaS and helps reduce cloud costs by simplifying infrastructure management.
If you’re looking to streamline your development process and focus on building innovative applications, PaaS is the perfect solution. It provides a fully managed environment with built-in tools for rapid deployment, scalability, and seamless integration, allowing your team to focus on what matters most – creating great software.
Ready to leverage Cloud Services for your business?
At Capital Numbers, we specialize in providing expert cloud engineering services tailored to your needs. Contact us today to unlock the full potential of cloud computing for your business!
What is Software as a Service (SaaS)?
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud service model that delivers software applications over the internet, typically on a subscription basis. SaaS allows businesses to access fully functional software without needing to install or maintain it on their infrastructure, offering a quick and efficient way to adopt cloud solutions for business.
Key Features:
- Subscription-Based Model: SaaS operates on a pay-as-you-go model, where businesses pay a recurring fee to use the software, eliminating large upfront costs.
- No Infrastructure Management: With SaaS, businesses do not need to manage hardware or software updates, as everything is handled by the service provider, allowing you to focus on your core business.
- Accessibility via Web Browsers: SaaS applications are accessible through any device with an internet connection and a web browser, enabling flexibility and remote work.
Common Use Cases:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): SaaS is commonly used for CRM software, which helps businesses efficiently manage customer data, sales, and marketing efforts.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): SaaS offers cloud-based ERP solutions to streamline business processes, including finance, HR, and supply chain management.
- Communication Tools: SaaS enables tools like email, video conferencing, and instant messaging, allowing teams to communicate effectively without managing the underlying infrastructure.
- Collaboration and Productivity Tools: Tools like Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 are SaaS solutions that help teams collaborate on documents, manage tasks, and stay productive from anywhere.
Examples of SaaS Providers:
- Salesforce: Salesforce is a leading CRM platform that helps businesses manage customer relationships and sales processes, offering powerful analytics and automation features.
- Slack: Slack is a team collaboration tool that facilitates messaging, file sharing, and app integrations, making team communication simpler and more efficient.
- Zoom: Zoom is a cloud-based video conferencing tool that allows businesses to host virtual meetings, webinars, and online collaborations.
If you’re looking for a hassle-free, cost-effective solution that eliminates the need for infrastructure management, SaaS is the way to go. It offers ready-to-use software applications that are easily accessible, secure, and updated automatically, allowing your business to focus on core operations without worrying about maintenance or upgrades.
You May Also Read: How Salesforce Industry Clouds Turn Business Challenges into Smart Solutions
IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS: How Do They Differ
When choosing between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, it’s essential to understand their key similarities and differences in cloud computing solutions, as each model serves distinct business needs. Here’s a breakdown of how these cloud service models compare:
Level of Control:
- IaaS: Offers the highest level of control over infrastructure, allowing businesses to manage and configure virtual machines, storage, and networks. You have the flexibility to install and configure software on your virtualized infrastructure.
- PaaS: Provides a more abstracted level of control, where businesses manage applications and data but leave infrastructure management to the platform. It’s ideal for businesses focused on development and deployment without handling infrastructure complexities.
- SaaS: Offers the least control, as businesses only use the software provided. There is no management or customization of the underlying infrastructure or application – users simply access the software through the Internet.
Type of Services Offered:
- IaaS: Offers foundational cloud computing services like virtual machines, storage, networking, and load balancing, ideal for businesses that need flexible and customizable infrastructure.
- PaaS: Provides a platform with development tools, frameworks, and services for building, deploying, and managing applications. It eliminates the need to manage infrastructure while focusing on software development and deployment.
- SaaS: Delivers fully managed software applications over the internet, such as CRM tools, email, or project management platforms, without requiring businesses to operate or maintain the software.
Target Users:
- IaaS: Primarily aimed at IT teams and businesses needing scalable infrastructure and more control over their resources. It’s ideal for cloud-native development or businesses migrating to the cloud.
- PaaS: Designed for developers and application teams who need to build, deploy, and manage applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. It’s perfect for businesses focusing on fast application development.
- SaaS: Targeted at end-users and businesses looking for ready-to-use software solutions that improve efficiency without worrying about maintenance or infrastructure.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: At a Glance
| Feature | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level of Control | High control over infrastructure (servers, storage, networking) | Moderate control (focus on application development) | Low control (software managed by provider) |
| Type of Service | Provides virtualized hardware resources (e.g., VMs, storage) | Provides a platform for building, deploying, and managing applications | Provides fully managed software applications for end users |
| Target Users | IT teams, system administrators, developers | Developers, application builders | End users, businesses |
| Customization | High customization (configure and manage infrastructure)High customization (configure and manage infrastructure) | Limited customization (focus on app features) | Minimal customization (focus on software use) |
| Examples | AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud | AWS Lambda, Google App Engine, IBM Cloud | Salesforce, Slack, Zoom |
| Use Cases | Hosting websites, virtual machines, data storage, and backup | App development, microservices, API management | CRM, email, collaboration, and communication tools |
| Management Responsibility | You manage the operating system, applications, and data | You manage the applications and data, provider handles platform | Provider manages everything, including updates and maintenance |
| Cost Structure | Pay-per-use based on resource usage | Subscription-based, pay for platform usage | Subscription-based, pay for software access |
You May Also Read: How Cloud Engineering Services Can Accelerate Your Business Growth
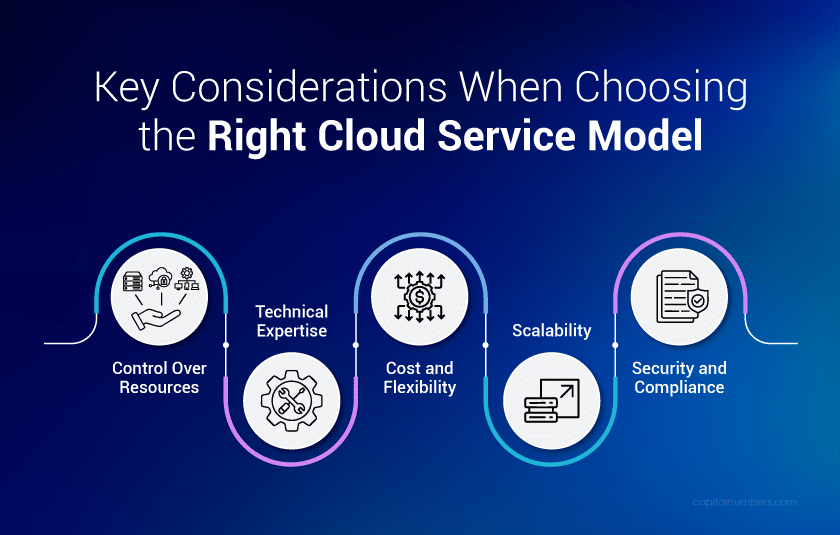
5 Key Considerations When Choosing the Right Cloud Service Model
Choosing the right cloud service model is an important decision for your business. With options like IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, each model has its benefits and drawbacks, so it’s important to know which works best for your needs.
1. Control Over Resources:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) gives you full control over your infrastructure, like servers and storage. If you want to focus on building applications without worrying about the underlying tech, Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a better choice. Software as a Service (SaaS) offers ready-to-use software with minimal control required.
2. Technical Expertise:
IaaS and PaaS need strong technical knowledge to manage the infrastructure or development platform. If you don’t have a tech-heavy team, SaaS is the easiest option, as the software is already set up and ready to use.
3. Cost and Flexibility:
IaaS offers flexible pricing based on what you use, which can be cost-effective for businesses that need customizable infrastructure. PaaS is great for app developers, saving time and costs by managing the platform for you. SaaS has fixed pricing, making it easy to budget, though it can get more expensive as you scale.
4. Scalability:
IaaS offers the best scalability, letting you easily increase or decrease resources based on your needs. PaaS is scalable for application development but may have some limitations. SaaS scales well with users but doesn’t allow much customization as your business grows.
5. Security and Compliance:
With IaaS, you control the security of your infrastructure and can customize it to meet your needs. PaaS offers platform-level security, but you are responsible for securing the applications you build. SaaS providers handle security, but you need to ensure they meet your compliance standards, especially for sensitive data.
Considering these factors will help you choose the right cloud service model for your business, whether it’s IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS, and ensure it supports your cloud solutions for business effectively.
You May Also Read: Cloud Computing in 2025: What’s Next for the Industry?
Bottom Line
Understanding the differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS is key to choosing the right cloud service model for your business. Each model provides different levels of control, customization, and management, so picking the right one is important for running your business smoothly and scaling effectively.
To make the right choice, consider your business’ specific needs – whether you need more control over infrastructure, a platform for building apps, or ready-to-use software. The right cloud model can help your business grow and stay ahead.
If you’re looking for comprehensive cloud solutions, Capital Numbers is here to help. We specialize in creating cloud solutions tailored to your business needs. Contact us today to get started!